Understanding Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Pricing Strategy
Related Articles: Understanding Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Pricing Strategy
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Pricing Strategy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Pricing Strategy
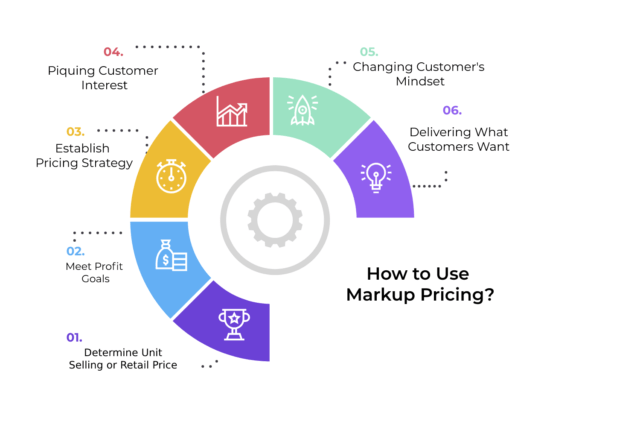
In the dynamic world of business, setting the right price for products or services is paramount to success. One of the fundamental strategies employed by businesses to determine prices is known as markup. This article delves into the concept of markup, exploring its intricacies, benefits, and considerations for effective implementation.
What is Markup?
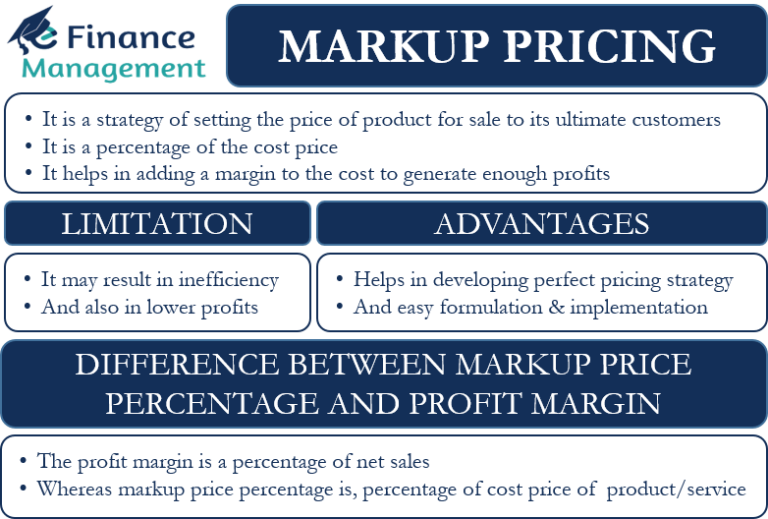
Markup represents the percentage added to the cost of a product or service to determine its selling price. Essentially, it’s a profit margin that businesses aim to achieve on each unit sold. The cost price serves as the foundation, and the markup percentage is calculated on this cost, ultimately dictating the final selling price.
Calculating Markup
The formula for calculating markup is straightforward:
*Markup Percentage = (Selling Price – Cost Price) / Cost Price 100**
For instance, if a product costs $10 to produce and is sold for $15, the markup percentage would be:
($15 – $10) / $10 * 100 = 50%
This implies that a 50% markup is applied to the cost price to arrive at the selling price.
Factors Influencing Markup
The markup percentage is not a static figure; it’s influenced by various factors, including:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The cost of producing or acquiring the product directly impacts the markup. Higher COGS often necessitate a higher markup to maintain profitability.
- Operating Expenses: Expenses incurred in running the business, such as rent, utilities, salaries, and marketing, also influence markup. Higher operating expenses necessitate a higher markup to cover costs.
- Competition: Market competition plays a significant role in determining markup. In highly competitive markets, businesses may need to adopt lower markups to remain competitive.
- Desired Profit Margin: Businesses strive to achieve a specific profit margin, which dictates the markup percentage. Higher profit margins generally require higher markups.
- Customer Value Perception: The perceived value of the product or service by customers can influence markup. Premium products or services often command higher markups due to their perceived value.
- Market Trends: Economic conditions and market trends can impact markup. During periods of inflation, businesses may adjust their markups to maintain profitability.
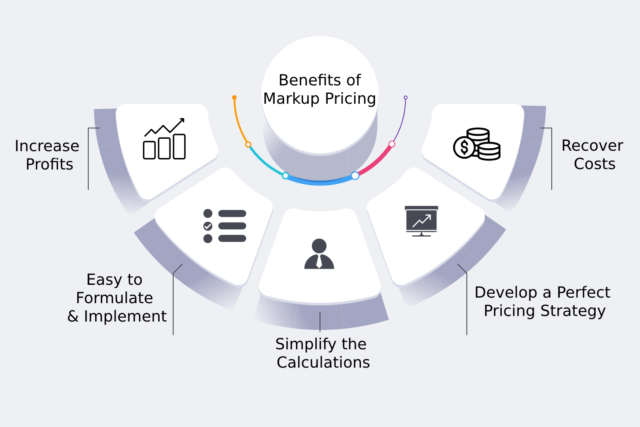
Benefits of Using Markup
Employing a markup strategy offers several benefits for businesses:
- Profitability: Markup ensures that businesses generate a profit on each unit sold, contributing to overall financial health.
- Pricing Consistency: Markup provides a consistent pricing framework, ensuring that all products or services within a category are priced according to a standard formula.
- Simplified Pricing: Calculating markup is relatively straightforward, making it an easy-to-implement pricing strategy.
- Cost Control: By focusing on the cost price and applying a specific markup, businesses can gain a better understanding of their cost structure and identify areas for cost reduction.
Considerations When Using Markup
While markup offers advantages, it’s essential to consider certain aspects:
- Market Analysis: It’s crucial to conduct thorough market research to understand competitor pricing and customer expectations.
- Cost Accuracy: Accurate cost accounting is essential to ensure the markup percentage is based on realistic cost figures.
- Flexibility: Markup should not be rigid; businesses need to be flexible in adjusting it based on market conditions and customer feedback.
- Value Perception: While markup is crucial for profitability, it should not be solely based on cost. Customer value perception and the perceived worth of the product or service should also be factored in.
Markup vs. Margin
Often, the terms "markup" and "margin" are used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts.
- Markup: Refers to the percentage added to the cost price to determine the selling price.
- Margin: Represents the profit percentage on the selling price.
To illustrate:
- If a product costs $10 and is sold for $15, the markup is 50% (as calculated earlier).
- The margin, however, would be 33.33% (($15 – $10) / $15 * 100).
Markup and Pricing Strategies
Markup is a fundamental component of various pricing strategies, including:
- Cost-Plus Pricing: This strategy involves adding a fixed markup to the cost of production.
- Value-Based Pricing: This approach focuses on the perceived value of the product or service to customers, setting the price accordingly.
- Competitive Pricing: Businesses base their prices on those of competitors, adjusting their markup to remain competitive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Markup
Q1: How do I determine the right markup percentage?
A1: The optimal markup percentage varies depending on factors such as industry, competition, and cost structure. It’s recommended to conduct market research and analyze competitor pricing to determine a suitable range.
Q2: Can I use different markup percentages for different products?
A2: Yes, businesses can use different markup percentages for different products based on factors like cost, demand, and perceived value.
Q3: How does markup impact my profit margin?
A3: A higher markup generally leads to a higher profit margin, but it’s essential to consider the impact on sales volume.
Q4: Should I adjust my markup during periods of inflation?
A4: Yes, businesses should adjust their markups during periods of inflation to maintain profitability.
Q5: What are some common markup percentages used in different industries?
A5: Markup percentages vary widely across industries. For example, restaurants typically have higher markups than grocery stores.
Tips for Using Markup Effectively
- Conduct thorough market research: Understand competitor pricing and customer expectations.
- Implement a cost accounting system: Ensure accurate cost tracking for effective markup calculation.
- Review and adjust markup regularly: Adapt to changing market conditions and customer feedback.
- Consider value perception: Don’t solely rely on cost; factor in the perceived worth of your product or service.
- Use markup as a tool for profitability, not just a means to increase prices.
Conclusion
Markup is a fundamental pricing strategy that enables businesses to determine selling prices based on cost and profit targets. Understanding the factors influencing markup, its benefits, and considerations is crucial for effective implementation. By applying a well-calculated markup, businesses can ensure profitability, maintain pricing consistency, and navigate the complexities of the market. However, it’s essential to remember that markup is just one piece of the pricing puzzle. Businesses must also consider customer value perception, market trends, and competition to set prices that resonate with their target audience and contribute to long-term success.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Pricing Strategy. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
