Demystifying Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Applying a 30% Margin
Related Articles: Demystifying Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Applying a 30% Margin
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Demystifying Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Applying a 30% Margin. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Applying a 30% Margin

In the world of business, understanding markup is crucial for ensuring profitability and sustainable growth. A markup represents the difference between the cost of a product or service and its selling price. It’s a percentage-based calculation that allows businesses to cover their operating expenses, generate a profit, and remain competitive.
This article delves into the concept of a 30% markup, exploring its significance, how to calculate it, and its implications for various business models.
Understanding the Concept of Markup
Markup is a fundamental concept in pricing strategy. It allows businesses to determine the selling price of their products or services based on their cost. The formula for calculating markup is:
*Markup = (Selling Price – Cost Price) / Cost Price 100**
A 30% markup signifies that the selling price is 30% higher than the cost price. For example, if a product costs $100 to produce, a 30% markup would result in a selling price of $130.
The Significance of a 30% Markup
A 30% markup is commonly used in many industries, including retail, manufacturing, and service sectors. It serves as a benchmark for profitability, ensuring that businesses can cover their expenses and generate a reasonable profit margin.
Benefits of a 30% Markup
- Profitability: A 30% markup allows businesses to generate a substantial profit margin, contributing to their overall financial health and sustainability.
- Covering Expenses: The markup covers operational costs such as rent, utilities, salaries, and marketing, ensuring that the business remains financially viable.
- Competitive Pricing: A 30% markup enables businesses to offer competitive prices while still maintaining profitability.
- Investment and Growth: Profit generated from a 30% markup can be reinvested back into the business, facilitating growth, expansion, and innovation.
Factors Influencing Markup
While a 30% markup is a common benchmark, the ideal markup percentage can vary significantly depending on several factors:
- Industry: Different industries have varying cost structures and competitive landscapes. For example, industries with high operating costs might require a higher markup percentage than those with lower costs.
- Product or Service Type: The complexity, value, and demand for a product or service can influence markup. Premium products or services often command higher markups.
- Competition: The level of competition in the market can affect pricing strategies. In highly competitive markets, businesses may need to lower their markups to remain competitive.
- Target Market: The purchasing power and preferences of the target market can influence pricing. Businesses targeting high-income customers might be able to charge higher markups.
- Economic Conditions: Inflation and other economic factors can impact pricing decisions. Businesses may need to adjust their markups to reflect changes in the cost of goods and services.
Calculating Markup: A Practical Example
Let’s illustrate how to calculate a 30% markup with a real-world example:
Scenario: A retailer purchases a dress for $50.
Calculation:
- Cost Price: $50
- Markup Percentage: 30%
- Markup Amount: $50 * 0.30 = $15
- Selling Price: $50 + $15 = $65
Therefore, the retailer would sell the dress for $65 to achieve a 30% markup.
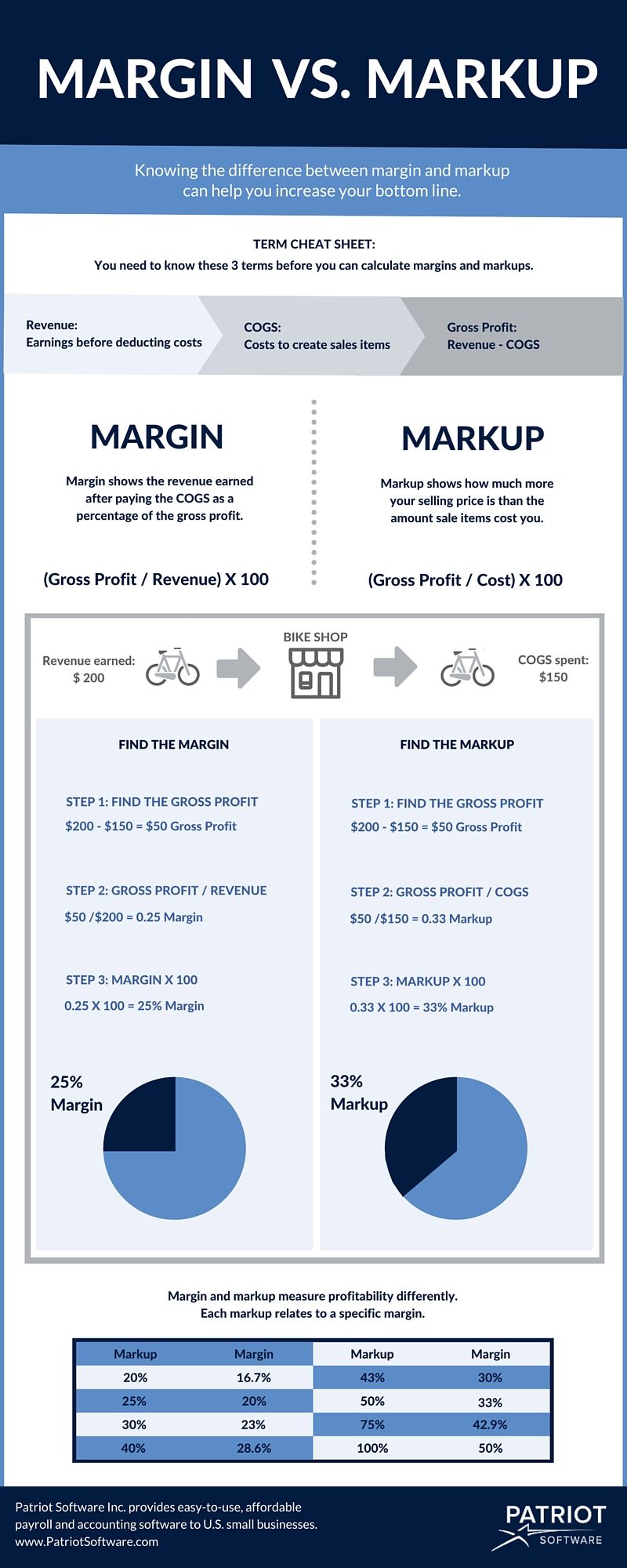
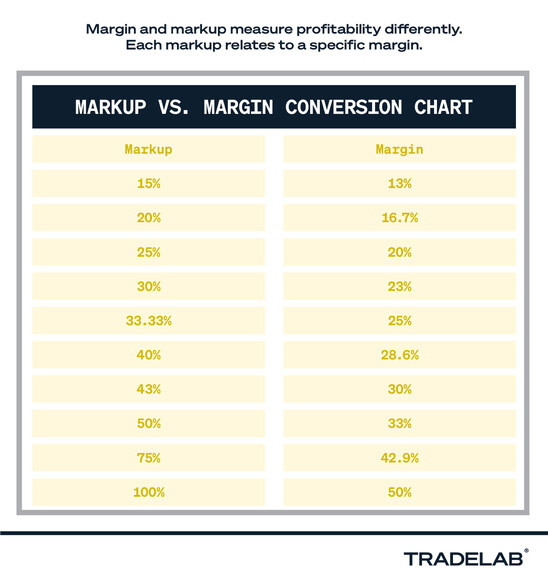
Markup vs. Margin: Understanding the Difference
It’s important to distinguish between markup and margin. While both relate to profitability, they represent different perspectives:
- Markup: The percentage difference between the cost price and the selling price.
- Margin: The percentage difference between the selling price and the cost price, expressed as a percentage of the selling price.
Calculating Margin from a 30% Markup
To calculate the margin from a 30% markup, use the following formula:
*Margin = Markup / (1 + Markup) 100**
In our previous example, the margin would be:
*Margin = 0.30 / (1 + 0.30) 100 = 23.08%**
Therefore, the retailer would have a 23.08% margin on the dress after applying a 30% markup.
Considerations When Applying a 30% Markup
While a 30% markup can be a viable strategy for many businesses, it’s crucial to consider several factors:
- Market Acceptance: The target market must be willing to pay the price determined by the 30% markup.
- Competitive Landscape: Businesses must remain competitive by comparing their markups to those of their competitors.
- Cost Management: Businesses need to control their costs to ensure that a 30% markup is sufficient to cover expenses and generate a profit.
- Flexibility: Businesses should be flexible in adjusting their markups based on market conditions, customer preferences, and competitor pricing.
FAQs about Markup
Q1: Is a 30% markup always the right choice?
A: A 30% markup is a common benchmark, but the ideal markup percentage can vary depending on factors like industry, product type, competition, and target market. It’s essential to conduct thorough market research and analyze competitors’ pricing strategies before setting a markup.
Q2: How can I determine the right markup for my business?
A: There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Consider your cost structure, target market, competitor pricing, and desired profit margin. Conduct a break-even analysis to determine the minimum markup required to cover your costs and generate a profit.
Q3: Can I increase my markup to increase my profit margin?
A: While increasing the markup can boost profit margin, it’s crucial to consider market acceptance. A high markup might deter customers, leading to decreased sales and overall lower profitability.
Q4: How does inflation affect markup?
A: Inflation can increase the cost of goods and services, impacting your cost price. Businesses may need to adjust their markups to compensate for rising costs and maintain profitability.
Q5: What are some tips for maximizing profitability with a 30% markup?
A:
- Cost Optimization: Focus on reducing your operational costs through efficient procurement, lean manufacturing, and streamlined processes.
- Value Proposition: Offer a strong value proposition to justify the price determined by the 30% markup.
- Customer Loyalty: Build strong customer relationships and loyalty programs to encourage repeat purchases and reduce customer churn.
- Sales and Marketing: Invest in effective sales and marketing strategies to attract new customers and increase sales volume.
Conclusion
Markup is a fundamental concept in business, allowing businesses to cover their costs, generate profits, and remain competitive. A 30% markup is a common benchmark, but the ideal markup percentage can vary depending on several factors. By understanding the concept of markup, businesses can make informed pricing decisions, optimize their profitability, and achieve sustainable growth. Remember to conduct thorough research, analyze competitors, and adjust your markup strategy based on market conditions and customer preferences.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Applying a 30% Margin. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
